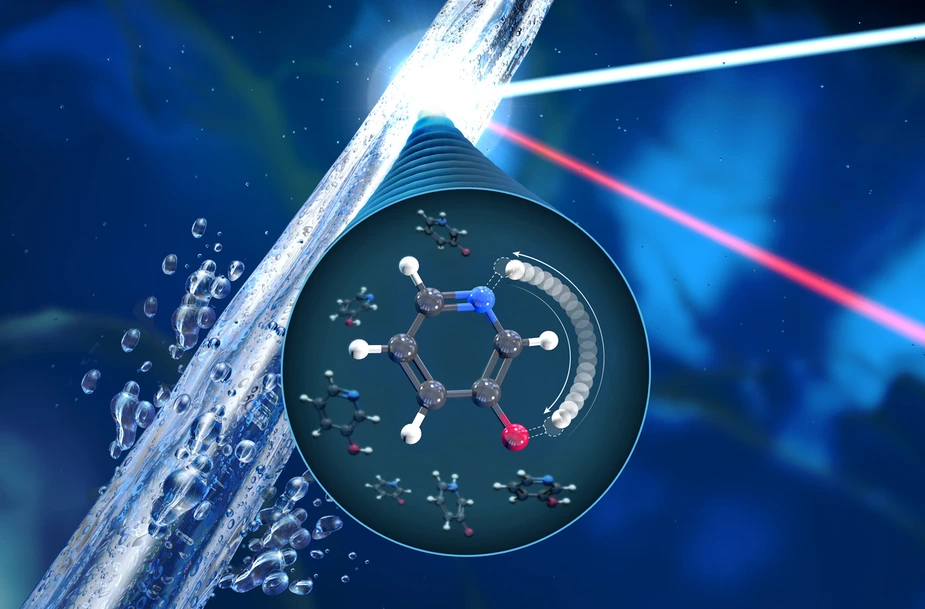
Unravelling tautomeric mixtures
Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) at BESSY II provides detailed information on properties and biological function
A team at HZB has developed a method of experimentally unravelling tautomeric mixtures. Based on resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) at BESSY II, not only proportions of the tautomers can be deduced, but the properties of each individual tautomer can be studied selectively. This method could yield to detailed information on the properties of molecules and their biological function. In the present study, now advertised on the cover of “The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters” the technique was applied to the prototypical keto-enol equilibrium.
Many (organic) molecules exist as a mixture of two almost identical molecules, with the same molecular formula but one important difference: A single hydrogen atom sits in a different position. The two isomeric forms transform into each other, creating a delicate equilibrium, a "tautomeric" mixture. Many amino acids are tautomeric mixtures, and since they are building blocks of proteins, they may influence their shape and function and thus their biological functions in organisms.
Until now: Mission impossible
Until now, it has been impossible to selectively investigate the electronic structure of such tautomeric mixtures experimentally: Classical spectroscopic methods “see” only the sum of the signals of each molecular forms - the details of the properties of the two individual tautomers cannot be determined.
Now at BESSY II: it works
A team led by HZB physicist Prof. Alexander Föhlisch has now succeeded in providing a method of experimentally unravelling tautomeric mixtures. Using inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) and a data processing/evaluation method newly developed at HZB, the individual proportions of the tautomers can be clearly deduced from the measured data. "We can experimentally separate the signal of each individual molecule in the mixture by X-ray scattering, which leads to a detailed insight into their functionality and chemical properties," says Dr. Vinicíus Vaz Da Cruz, first author of the paper and postdoc in Föhlisch's team.
"Specifically, we measure a pure spectrum of each tautomer, taking advantage of the element specificity and site selectivity of the method," Vaz Da Cruz explains. This allowed them to fully characterise the components in the tautomer mixture.
New insights into biological processes
In the present study, the technique was applied to the prototypical keto-enol equilibrium of 3-hydroxypyridine in aqueous solution. The data were obtained at the EDAX terminal station at BESSY II.
These results provide experimental evidence for concepts that have previously only been discussed theoretically in the literature. They are particularly interesting to enlighten and understand important biological processes such as the interaction between nucleoid bases of the DNA, metabolic conversion of fructose into glucose, or the folding of proteins.
Publication
Targeting Individual Tautomers in Equilibrium by Resonant Inelastic X‑ray Scattering
Vinícius Vaz da Cruz, Robby Büchner, Mattis Fondell, Annette Pietzsch, Sebastian Eckert, and Alexander Föhlisch
The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (2022). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c03453
Contact:
Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
Institute Methods and Instrumentation for Synchrotron Radiation Research
Prof. Dr. Alexander Föhlisch
Phone +49 30 8062-14985
Email alexander.foehlisch(at)helmholtz-berlin.de
Dr. rer. nat. Vinícius Vaz da Cruz
Phone +49 30 8062-13494
Email vinicius.vaz_da_cruz(at)helmholtz-berlin.de
Press release HZB, 17 March 2022