Absolute measurement of electronic properties with a THz nanoprobe
At PTB, a novel calibration approach for scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy has been developed
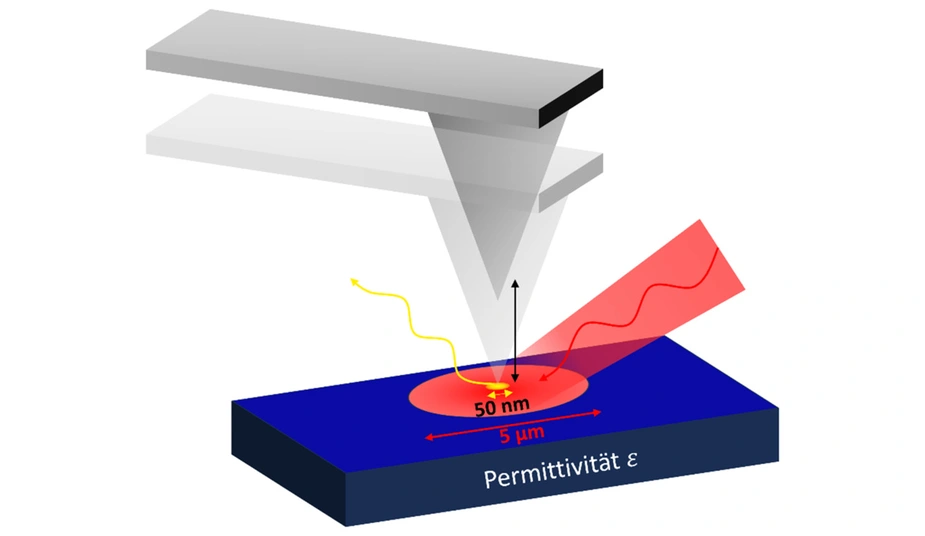
In scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM), THz radiation (e.g. from the electron storage ring MLS) is focused onto a metallised probe to enable THz-spectroscopy below the diffraction limit on nanoscale material systems, with the probe acting as an optical antenna. The light emitted or scattered by the probe varies with the dielectric conductivity (permittivity) of the sample. The permittivity is therefore encoded in the scattered light.
To simplify the complex near-field interactions between probe and sample that occur in this method and to extract the permittivity precisely, a novel calibration approach was developed. Here, the scattered light is calibrated to known permittivities. In contrast to conventional stationary calibration methods used in microwave technology, this approach takes into account the modulation of the distance between the s-SNOM probe tip and the sample. This is necessary to distinguish the scattered light in the vicinity of the tip from the incident light and to achieve a high spatial resolution. The calibration method uses a Fourier series representation of the scattered light based on the non-linear dependence on the probe tip distance and takes into account several harmonics of the sampling frequency. The method was tested on a commercial system and the calibration enabled reliable permittivity determination for silicon samples with different doping levels.
The new calibration approach makes it possible to precisely determine the local permittivity and thus the local charge carrier density and mobility. The results offer new perspectives for the application of the s-SNOM technique in the contactless electrical analysis of nanostructures.
Publication:
Calibration method for complex permittivity measurements using s-SNOM combining multiple probe tapping harmonics
D. Siebenkotten et al., Opt. Express, 32, 23882
https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.523785
Contact:
Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)
Bernd Kästner
Working Group 7.11: IR Spectrometry
Bernd.Kaestner(at)ptb.de
Source: PTB, 11 November 2024